Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits


 This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia-Clemente
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia-Clemente
Briefing Document: Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore
1. Overview
This document summarizes key information extracted from a webpage hosted by "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore." The primary focus is a specific applet, the "Model Comparison Question Generator," which is a JavaScript HTML5 application designed for educational purposes. However, the page also serves as a portal to a vast library of other interactive physics and math simulations, projects, and resources developed within this open-source initiative.
2. "Model Comparison Question Generator" Applet
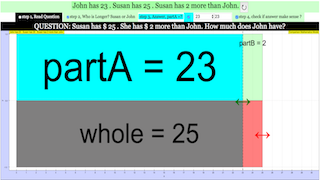
- Functionality: This applet is designed to generate comparison questions, likely focusing on "Part Part Whole Model Comparison" in mathematics, as indicated in the "For Teachers" section which links to related research. The "Addition and Substraction" label in the breadcrumbs implies the applet's scope.
- Technology: It's built using JavaScript and HTML5, making it accessible in web browsers without requiring plugins.
- Embeddable: The provided iframe code indicates that the applet can be easily embedded into other web pages.
- Credits: The applet was created by Francisco Esquembre and Felix J. Garcia-Clemente.
- Version: The link provided suggests that this model is a HTML5 implementation of an earlier Java version (http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2017/12/part-part-whole-model-comparison.html).
3. Broader Context: Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore
- Mission: The website is a repository of open educational resources (OER), focused primarily on interactive simulations for physics and mathematics education. The initiative emphasizes open-source principles, allowing educators and learners to freely use and adapt the resources.
- Technology: The simulations are primarily built using Easy JavaScript Simulations (EJS), a tool that facilitates the creation of interactive models for STEM education. Many of the simulations appear to be conversions of older Java-based EJS models.
- Target Audience: The materials are clearly aimed at both teachers and students, providing interactive tools to enhance teaching and learning of physics and mathematics concepts.
- Content Depth: The range of simulations is incredibly diverse, spanning from basic math concepts (e.g., fractions, number properties) to complex physics topics (e.g., electromagnetism, quantum mechanics). It also includes interactive games, data analysis tools, and video-based modeling resources.
- Licensing: The content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, allowing for broad sharing and adaptation. Commercial use of the EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library requires adherence to a separate license from the University of Murcia (UM).
4. Key Themes and Ideas
- Interactive Learning: A strong emphasis on interactive simulations and models to facilitate hands-on, experiential learning in STEM fields. This is seen in the sheer number and diversity of applets.
- Open Source and OER: A commitment to open-source principles and the creation of openly licensed educational resources. This fosters a collaborative environment and allows for wider access to quality educational materials.
- Technology Integration: A clear focus on leveraging technology to create innovative learning experiences. JavaScript, HTML5, and WebGL are frequently used to deliver these interactive experiences.
- Adaptability: The use of JavaScript/HTML5 means that the resources are adaptable to multiple platforms (desktops, tablets, and mobile phones) and that simulations can be easily embedded into other web pages or learning management systems.
- Evolving From Java: Many of the descriptions include details of how older java-based simulations were converted to the current JavaScript based versions.
5. Examples of Other Resources and Projects:
The provided list of applets demonstrates the extensive range of simulations and tools available. Here are a few examples to illustrate the diversity:
- Mathematics: "Add and Subtract Fractions," "Comparing Fractions," "More than Less than Question Generator", "Primary School Numbers from 1 to 100."
- Physics: "Projectile Motion with Comparison," "Mass Spectrometer," "Faraday Law," "Doppler Effect Sound Wave," "Photoelectric Effect," "Secondary Kinematics or Moving Car 1D."
- Data Analysis and Modeling: "Modeling Instruction Data Fitting," "Tracker SHM 350g Initial Extension Tension Weight Model", "Video Tracker."
- Interactive Games: "Math Battle: Add or Multiply?" "Catch the Recyclables!"
- Pedagogical Tools: "Student Learning Space master quiz Vector Components QUIZ JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model", "Titration Curve Generator."
- Specific Projects/Awards: References to "Ministry of Education GOLD Innergy Award" for the "Open Source Physics at Singapore" project, as well as UNESCO and other awards highlight the recognized quality and importance of the work.
6. Notable Collaborators and Contributors Many of the applets and resources are attributed to specific developers and contributors. In addition to those credited with the "Model Comparison" tool itself, the following names stand out from their numerous contributions across the resources: * Francisco Esquembre * Felix J. Garcia-Clemente * Wolfgang Christian * Loo Kang WEE * Leong Tze Kwang * Boon Chien
7. Potential Areas of Interest
- Educators: The site offers a wealth of interactive simulations that can be readily integrated into various curricula. Teachers could use this as a basis for lesson planning, demonstrations, and student activities.
- Students: The resources provide a fun and engaging way to learn and explore STEM concepts.
- Researchers: The open-source nature of the project, and the data generated from its use, allows opportunities for research into effective methods of teaching with simulations.
- Developers: The code and simulation files may also be useful to developers working in the field of educational simulation.
8. Conclusion
The "Model Comparison Question Generator" applet, while a focused resource, serves as an entry point to a much larger project in open-source educational resource development. The "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" initiative has clearly created a substantial collection of high-quality interactive STEM resources, demonstrating a commitment to both open-source principles and the use of technology to enhance teaching and learning. The breadth of resources available makes this a powerful tool for both teachers and students across a range of educational levels.
Model Comparison Study Guide
Quiz
Instructions: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What is the primary function of the "Model Comparison Question Generator" applet?
- What type of mathematical operation does the applet specifically focus on?
- Who are the primary creators credited with developing this applet?
- Besides math, what other fields might this applet be relevant to?
- What is the name of the organization that hosts this resource?
- Where can you embed this model into a webpage?
- What is one of the suggested learning goals for this applet?
- What is one of the technologies used to develop this applet?
- What is the purpose of the "Part Part Whole Model Comparison" mentioned in the "For Teachers" section?
- What is the type of license associated with the content on the website?
Quiz Answer Key
- The primary function of the "Model Comparison Question Generator" applet is to help users practice and understand the comparison of mathematical models, particularly part-part-whole relationships. It allows for the generation of different comparison questions based on the user's needs and skill level.
- The applet specifically focuses on addition and subtraction as the mathematical operations for model comparison. This is highlighted in the applet description as well as the link provided in the 'For Teachers' section.
- The primary creators credited with developing this applet are Francisco Esquembre and Felix J. Garcia-Clemente, as listed in the credits section of the webpage.
- While the applet focuses on mathematical concepts, it can be relevant to any field that uses part-part-whole analysis, such as resource management or basic statistics. The applet's focus on comparison is also relevant to problem-solving.
- The name of the organization that hosts this resource is "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore."
- This model can be embedded into a webpage by using the provided iframe code. The embed code allows the applet to be viewed on a different website.
- One suggested learning goal for this applet includes understanding the Part Part Whole Model Comparison. It's a core concept in mathematics that the applet supports and the material suggests.
- The technologies used to develop this applet include JavaScript and HTML5, as it is specified that it is a JavaScript HTML5 applet.
- The "Part Part Whole Model Comparison" is a visual and conceptual framework for understanding how individual parts relate to the whole and to each other. It's used as a foundation for developing mathematical thinking and solving problems.
- The content on the website is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License.
Essay Questions
Instructions: Choose one of the following questions and write a well-structured essay, drawing from the source material provided.
- Discuss the significance of the "Model Comparison Question Generator" within the context of open educational resources, considering its potential impact on teaching and learning.
- Analyze the various types of interactive simulation applets listed on the website, explaining how they contribute to a broader understanding of science and math.
- How can the integration of JavaScript HTML5 applets, like the Model Comparison Generator, enhance engagement and interactivity in online educational content?
- Based on the listed tools, discuss how this site supports diverse learning across multiple disciplines of mathematics and science.
- Explain the different types of licenses associated with this website and their importance for an open-source model.
Glossary of Key Terms
Applet: A small application, often written in Java or JavaScript, that runs within another application, like a web browser.
JavaScript: A popular programming language used to create interactive effects within web browsers.
HTML5: The latest version of Hypertext Markup Language, used to structure and present content on the web. HTML5 is often used in conjunction with Javascript for functionality.
Open Educational Resources (OER): Educational materials that are freely available for anyone to use, reuse, adapt, and share.
Simulation: A computer model of a real-world system or process, often used for educational or training purposes.
Part-Part-Whole Model: A mathematical concept that visualizes the relationship between parts of a whole object or amount, often used in primary mathematics.
Model Comparison: The process of examining and contrasting different representations of a mathematical or scientific concept to gain a deeper understanding.
Iframe: An HTML element used to embed another HTML page into the current page.
Creative Commons License: A type of license that allows creators to share their work while retaining some rights, specifying how others can use the material.
Easy JavaScript Simulations (EjsS): A modeling tool used to create interactive simulations in Java, which can then be converted into Javascript for the web.
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
Part Part Whole Model Comparison
 |
| https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsgx/index.php/579 |
Research
[text]
Video
[text]
Version:
Other Resources
FAQ: Open Source Physics Simulations and Educational Resources
- What is the purpose of the Model Comparison Question Generator applet and similar tools hosted on this platform?
- The primary purpose of the Model Comparison Question Generator applet, as well as the numerous other simulations and tools provided, is to support interactive and engaging learning in mathematics, physics, and other STEM subjects. They facilitate exploration and comparison of different models, fostering a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts through direct interaction. These tools can be used in classrooms or for individual study. The specific example given for "Model Comparison" focuses on a "Part Part Whole" model, suggesting it's designed to help students visualize and understand the relationships between different parts and the whole, particularly when adding and subtracting.
- What types of subjects are covered by these interactive simulations and resources?
- The platform hosts a wide range of interactive simulations and resources covering diverse topics in STEM, notably including: mathematics (e.g., fractions, algebra, geometry), physics (e.g., mechanics, electromagnetism, waves, optics, thermodynamics, quantum physics), and chemistry (e.g. titrations, atomic structure). The broad scope of the topics suggests an effort to support both primary and higher-level secondary and tertiary-level education.
- How are these simulations created and what technologies are used?
- Many of the interactive simulations are created using Easy JavaScript Simulations (EJS), a tool that allows for the design and development of open-source educational simulations. This software helps teachers and educators create interactive models. The simulations run in web browsers using JavaScript and HTML5, making them accessible across various devices without the need for specific software installations.
- What is the "Part Part Whole Model Comparison" mentioned, and how is it related to the applet?
- The "Part Part Whole Model Comparison" is a specific pedagogical approach in mathematics, often used in primary school. It emphasizes understanding the relationship between parts and a whole when dealing with addition and subtraction problems. The Model Comparison Question Generator applet uses this model to help students visualize these relationships, making abstract math concepts more concrete and understandable.
- What is the "Open Source Physics @ Singapore" initiative, and what are its key aims?
- Open Source Physics @ Singapore is an initiative dedicated to creating and sharing open educational resources (OER) in physics and other STEM areas. The primary aim of this project is to make high-quality, interactive learning materials freely available to students, teachers, and anyone interested in learning. They utilize open-source tools and practices to enhance the learning experience and encourage collaboration and innovation in education.
- Can these simulations be used in different learning environments?
- Yes, these simulations are designed to be adaptable to various learning environments. They can be used in traditional classroom settings as instructional tools, in blended learning environments to complement traditional teaching methods, and for individual self-paced learning. The accessibility through web browsers also makes them usable at home or in remote learning settings. Many of the resources are designed for specific grade levels, from primary to university, indicating their suitability for a wide range of learners.
- What kinds of resources beyond interactive simulations are available?
- In addition to interactive simulations, the platform also includes articles, learning goals, video demonstrations, and links to related research. There are also interactive quizzes. This indicates that the platform strives to offer a comprehensive educational experience rather than merely a collection of single simulations. There are also resources relating to professional development for teachers on how to use these tools.
- How can educators get involved with or contribute to this initiative?
- The platform strongly encourages collaboration and community contribution. While the main source document doesn't explicitly call out an avenue for contribution, the use of the Creative Commons license on the content along with the emphasis on open-source tools implies that those interested in contributing may adapt, share, and use the resources as long as proper attribution is given, and derivative works are shared under the same license. The mention of workshops and collaborations suggests other avenues for engagement could exist. Educators can also benefit from resources on how to use these simulations in class.